
Scarring alopecia, also known as cicatricial alopecia, is a type of hair loss that is caused by inflammation and results in damages to hair follicles. The damaged hair follicles are replaced by scar tissue giving a patchy appearance. There are 2 types of scarring alopecia: primary cicatricial alopecia and secondary cicatricial alopecia. This condition can be caused by various factors such as autoimmune disorders, infections, burns. Etc. A thorough examination by a dermatologist is requirement to determine the exact cause and find the appropriate solution.
Scarring alopecia, also known as cicatricial alopecia, is a group of rare hair loss disorders that often present a unique set of challenges for individuals affected by it. Unlike more common forms of alopecia, such as androgenetic alopecia (male pattern baldness) or alopecia areata, scarring alopecia is characterized by permanent hair loss due to the destruction of hair follicles. The destroyed hair follicles are replaced with scar tissue, making it impossible for hair to regrow. The progression of scarring alopecia can vary significantly, either developing gradually and going unnoticed for years or rapidly advancing within just a few months.
The underlying causes of scarring alopecia can be diverse, which emphasizes the need to consult a dermatologist specialized in hair loss to identify the specific type of scarring alopecia so a suitable treatment plan can be applied. Autoimmune disorders such as lichen planopilaris and discoid lupus erythematosus can trigger the immune system to attack hair follicles, leading to scarring alopecia. Infections, like bacterial or fungal infections of the scalp, can result in inflammation and scarring, ultimately causing hair loss. Trauma, such as physical injury or burns to the scalp, can also disrupt hair follicles and lead to scarring.
Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are vital for managing the condition and potentially preserving existing hair. If you suspect you may be experiencing symptoms of scarring alopecia, it's advisable to consult a dermatologist such as Dr. Civas or Dr. Akpınar, for a thorough evaluation and a personalized treatment plan. It's important to note that this condition is neither infectious nor hereditary, and it can affect individuals of any age, highlighting the significance of awareness and early intervention.
Cicatricial alopecia, or scarring alopecia, comprises two primary categories: primary cicatricial alopecia and secondary cicatricial alopecia. These distinct classifications represent unique pathways to hair loss, each with its own set of causes and characteristics. Primary cicatricial alopecia is characterized by inflammation directly targeting the hair follicles, resulting in their destruction and replacement with scar tissue, leading to permanent hair loss. In contrast, secondary cicatricial alopecia occurs when other factors, such as physical trauma, burns, or infections, disrupt the hair follicles, triggering inflammation and ultimately scarring. Recognizing these categories is crucial for accurate diagnosis and the development of appropriate treatment strategies for patients affected by these challenging hair disorders.
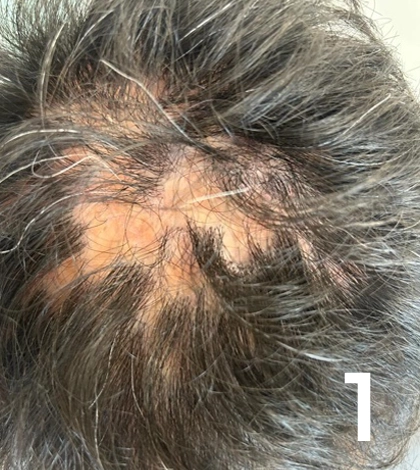
Alt: Close-up of a patient suffering from lichen planopilaris, a type of primary cicatricial alopecia. The patient has visible scarring and bald spots.
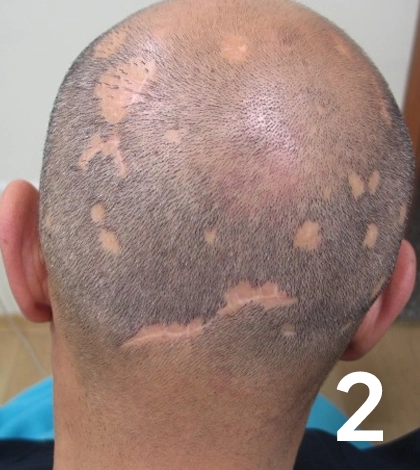
Alt: Picture of a patient suffering from Foliculitis decalvans showing the scars caused by the condition.
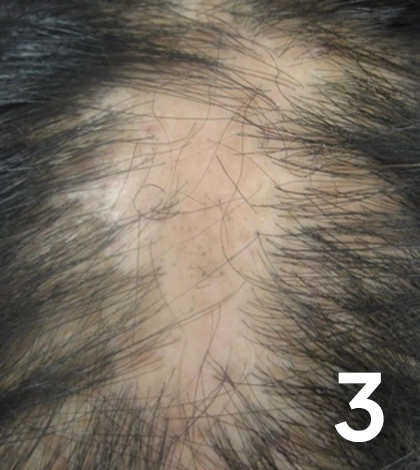
Alt: Close-up of a patient suffering from hair loss due to lichen planopilaris.
Primary cicatricial alopecia, a subset of scarring alopecia, is a complex and often perplexing condition that primarily affects the hair follicles themselves, causing their permanent destruction and replacement with scar tissue. This type of alopecia is distinct from secondary cicatricial alopecia, as it arises from intrinsic factors, often autoimmune or inflammatory in nature, that directly target the hair follicles.
The classification of primary cicatricial alopecia has been a subject of debate within the medical community, as many of these disorders exhibit overlapping clinical and histologic features, making it difficult to draw clear lines between them.
In 2001, the North American Hair Research Society conducted a workshop aimed at developing a provisional classification for primary cicatricial alopecias, grouping them based on their underlying characteristics:
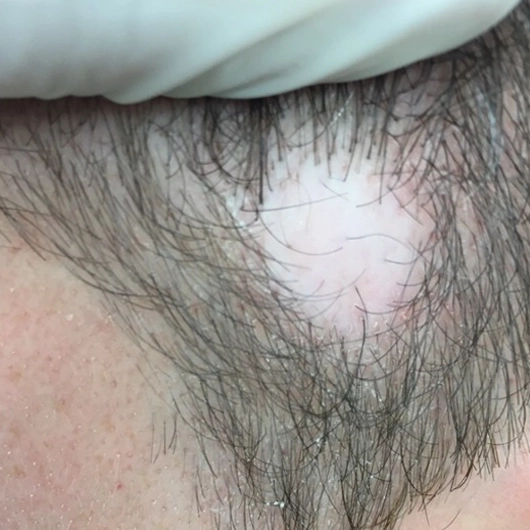
Alt: A close up of a person suffering from hair loss due to secondary cicatricial alopecia
Secondary cicatricial alopecia represents a distinctive category within scarring alopecia, wherein hair follicles' destruction is an indirect consequence of various external factors, such as trauma, infections, burns, or tumors. Unlike primary cicatricial alopecia, the underlying causes of secondary cicatricial alopecia are external in nature, often initiating inflammation and eventual destruction and scarring of the hair follicles.
Secondary cicatricial alopecia is classified into several subgroups based on the diverse underlying causes and clinical presentations:
Recognizing the symptoms of scarring alopecia is the first step in addressing this challenging hair disorder. Early diagnosis is crucial to slow the progression of the disease and preserve existing hair. With early diagnosis and appropriate intervention, it is possible to manage the condition and improve the lives of those affected by scarring alopecia.
Below is a list of symptoms that are associated with and can help diagnose scarring alopecia:
If you suspect you may be experiencing symptoms of scarring alopecia, seeking consultation with a dermatologist or a hair specialist is highly recommended to determine the specific subtype and commence a personalized treatment plan.
Diagnosing scarring alopecia is a process that requires careful evaluation by a skilled dermatologist. The diagnostic journey begins with a comprehensive medical history and a thorough clinical examination. Patients are encouraged to provide insights into their personal and family medical histories, highlighting any relevant information that could shed light on the potential causes of their hair loss. A clinical examination involves the careful inspection of the scalp and affected areas, taking into account key symptoms such as hair loss, redness, itching, and burning sensations, visible bumps, pimple-like lesions, and scaliness in bald patches.
A definitive diagnosis of scarring alopecia often requires a scalp biopsy, considered the gold standard for confirming the condition. During this procedure, a small sample of affected scalp tissue is collected for examination under a microscope. This biopsy helps determine the specific subtype of scarring alopecia and offers insights into the extent of inflammation and scarring present in the affected area. Scalp biopsy specimens should be at least 4 mm in diameter and should extend into the fat, providing an accurate representation of the affected tissue. Additionally, performing a scalp biopsy is not only crucial for diagnosis but also for assessing the degree of inflammation and injury to the stem cell region, aiding in the formulation of an appropriate treatment plan.
In some cases, particularly when an underlying cause such as an autoimmune condition is suspected, laboratory tests may be recommended. Blood tests can help identify specific antibodies and inflammatory markers associated with autoimmune disorders, aiding in the diagnostic process.
Accurate diagnosis is essential for tailored treatment strategies that can help slow the progression of the condition and preserve existing hair.
If you're experiencing the symptoms of scarring alopecia or seeking a definitive diagnosis, we encourage you to contact Civas Hair Transplant Clinic. Our expert team of dermatologists and specialists is dedicated to providing accurate diagnoses and personalized treatment plans. Don't wait; take the first step towards understanding and managing your condition. Contact us now to schedule a consultation and embark on your journey towards healthier, more confident hair. Early intervention is the key to effective management.
Scarring alopecia is a complex and challenging condition, but there are various treatment strategies available to help manage its symptoms and potentially slow down the progression of hair loss. Recognizing the specific subtype of scarring alopecia is vital for tailoring treatment approaches, and early intervention is key.
Here are some of the primary treatment options and approaches for addressing scarring or cicatricial alopecia:
It's important to recognize that treatment plans for scarring alopecia, especially primary cicatricial alopecia, should be personalized to suit the patient's specific needs and the subtype of the condition. Dermatologists, such as the ones at Civas Hair Transplant Clinic in Turkey, play a crucial role in evaluating each case and recommending the most appropriate course of action.
While treatment approaches are available to manage the symptoms and slow the progression of scarring/cicatricial alopecia, the prospect of regaining a full head of hair may seem elusive to those affected. However, there is hope, and hair transplant for scarring alopecia, not only holds the promise of hair regrowth but also the restoration of self-confidence for individuals grappling with this condition.
It's essential to note that the success of hair transplant surgery in individuals with scarring alopecia is contingent on the management of the disorder. This is why a disease-free period of at least one year is typically required before hair restoration surgery can be considered. The condition of the patient must be stable, and the scalp must be inflammation-free to ensure the best possible outcome. Hair transplant surgery not only offers the potential for regrowth but also a renewed sense of self-assuredness for patients. living with scarring alopecia.
Dr. Ekrem Civas stands out as not only a top hair surgeon in Turkey but also as a distinguished academician. Fueled by his natural curiosity, he continually seeks ways to enhance the techniques employed during hair transplant procedures and explores potential improvements that could lead to better results and greater patient satisfaction. Dr. Ekrem Civas' extensive studies and research on scarring alopecia have played a pivotal role in shedding light on the intricacies of this challenging hair disorder.
In 2018, he teamed up with colleagues to study 9 individuals diagnosed with primary cicatricial alopecia. Before starting the study, it was ensured that the patients' conditions had stabilized, and the disease was in an inactive state. Their main objective was to see how effective and successful FUE Hair Transplant was in treating primary cicatricial alopecia. For more details on this study, you can check out the following link: https://jag.journalagent.com/turkderm/pdfs/TURKDERM_52_3_85_90%5BA%5D.pdf
Following his work with individuals suffering from primary cicatricial alopecia, Dr. Civas initiated a study in 2019 that centered on 45 patients with secondary cicatricial alopecia. The primary objective of this research was to assess the outcomes of using hair transplant surgery as a treatment method for patients with secondary cicatricial alopecia. For additional information regarding this research study, you can refer to the following link: https://journals.lww.com/tjps/Fulltext/2019/27040/Clinical_Experience_with_Hair_Transplantation_for.3.aspx
Dr. Civas and Dr. Akpınar share a collaborative bond that extends beyond the operating room, encompassing their academic pursuits as well. In 2022, they jointly co-authored two articles focusing on cicatricial alopecia, titled 'Approach to Scalp Scars' and 'Innovations in Cicatricial Alopecia.' These articles delve into surgical interventions, such as hair transplantation, for individuals with primary and secondary cicatricial alopecia. Additionally, they explore supplementary and innovative treatments that can be applied when conventional approaches prove inadequate or insufficient.
For additional information on these research papers, you can refer to the following links:
Dealing with scarring alopecia can be a distressing and challenging experience. One question that often arises among individuals facing this condition is whether scarring alopecia can spontaneously stop or resolve without intervention. The answer to this question varies based on several factors, including the underlying cause of the alopecia and the stage at which it is diagnosed.
In some cases, especially when the scarring alopecia is caused by a reversible factor, it may halt or resolve on its own. This is known as 'spontaneous remission.' However, it's important to note that not everyone's scarring alopecia will naturally resolve without treatment. For example, certain medications or external factors that triggered hair loss may be discontinued, leading to a cessation of the alopecia. However, in the majority of cases, scarring alopecia is a progressive condition characterized by the permanent destruction of hair follicles due to inflammation and scarring. Once the hair follicles are replaced by scar tissue, they typically do not regenerate naturally.
It's crucial to note that early diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent further progression of the condition. Even though scarring alopecia may or may not spontaneously stop on its own, seeking specialized medical care from dermatologists who can help manage the inflammation and minimize the scarring is vital. The sooner the condition is diagnosed and addressed, the better the chances of controlling it and preventing further hair loss.
Stress is a common factor in many health conditions, including hair loss, but can it directly cause scarring alopecia? Scarring alopecia is primarily linked to inflammation and the destruction of hair follicles, making it different from the more common stress-related hair loss, such as telogen effluvium. While stress alone doesn't directly cause scarring alopecia, it can play a role in exacerbating or triggering certain types of scarring alopecia.
Stress can lead to or worsen hair loss in various ways. High stress levels can weaken the immune system, which may contribute to the inflammation associated with some types of scarring alopecia. Additionally, stress can result in hair-pulling behaviors, which can damage hair follicles and lead to scarring. It's important to recognize that the relationship between stress and scarring alopecia is complex and varies from individual to individual.